Water Resource Management
Water Risk Assessment and Identification of High Water Stress Areas
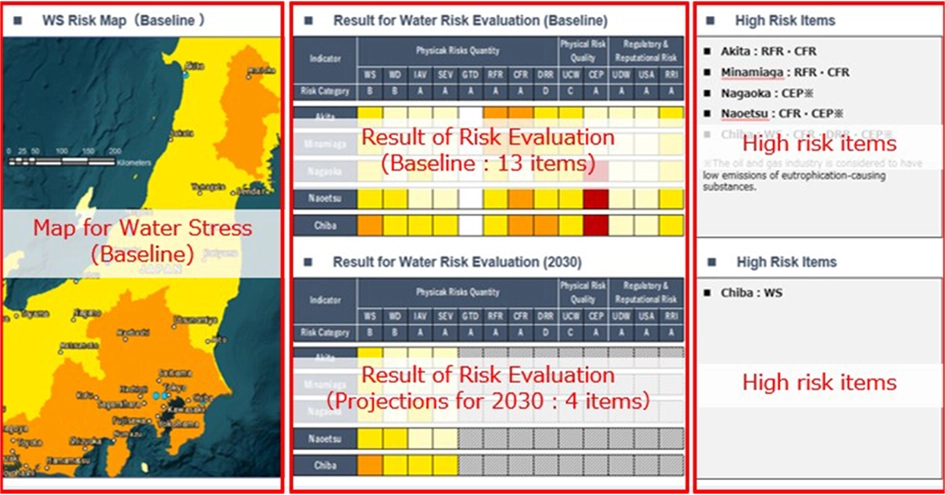
INPEX annually checks the water risk in the areas where its operator projects are located using Aqueduct, a water risk mapping tool developed by the World Resources Institute (WRI). The water risks we check include dependencies on water resources, impacts of our projects, potential future changes in water demand and quality, future potential regulatory changes at a local level, and reputation from external stakeholders. In FY2024, to further observe and promote our commitments, we also established "Maintain zero freshwater withdrawal in high water stress areas" as a Group-wide measurable quantitative target. As of the end of 2024, we are operating five oil and gas projects in production and one project under development as the operator. Among these, the Abadi Project, currently under development, is located in areas of high water stress. For this project, we are planning to install a seawater desalination plant. Therefore, no freshwater will be taken from the project area. Additionally, the exploration project at Onshore Block 4 in Abu Dhabi is also located in areas of high water stress. However, we procure water from a supplier that uses seawater desalination, no freshwater is being obtained from groundwater and such. In FY2024, we achieved our target of zero freshwater withdrawal in high water stress areas.
Since local water risks are influenced by various factors and change over time, we will continue to regularly identify water risks. If we find water risk to be high, we will plan and implement additional measures according to a mitigation hierarchy.
Indicators |
Indicator name |
Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Physical risks quantity |
WS |
Water stress |
WD |
Water depletion |
|
IAV |
Interannual variability |
|
SEV |
Seasonal variability |
|
GTD |
Groundwater table decline |
|
RFR |
Riverine flood risk |
|
CFR |
Coastal flood risk |
|
DRR |
Drought risk |
|
Physical risks quality |
UCW |
Untreated connected wastewater |
CEP |
Coastal eutrophication potential |
|
Regulatory and reputational risk |
UDW |
Unimproved/no drinking water |
USA |
Unimproved/no sanitation |
|
RRI |
Peak RepRisk country ESG risk index |
Risk map of domestic 2024 risk assessment results and 2030 projections
Efforts Contributing to Efficient Water Use
We conducted a water balance survey to identify water usage and improve water efficiency in each operator project. The survey results were used to understand in detail and analyze water usage for each facility and process. We aim to keep reducing water consumption and improve wastewater quality while reflecting the insights gained from our understanding and analysis.
Use of Freshwater
Annual Freshwater withdrawal in Japan and overseas
Unit: thousand ㎥
As one of water resources we utilize in our business operations, we recognize the freshwater withdrawal management to be a major issue in our water management. We have been working to reduce our impacts on water resources by managing the water withdrawal of our operator projects in Japan and overseas as well as the discharge of produced water arising from oil and natural gas production. Our operator project sites use freshwater (tap water, industrial water, and groundwater) mainly as coolants and for power generation and excavation work. In FY2024, the volume of freshwater used across the INPEX Group totaled 1,590 thousand cubic meters.
In addition to using groundwater for normal cooling and drilling operations in Japan, we also use it for melting snow in winter. We are also taking action to reduce our freshwater consumption, including by adopting a circulating system for cooling water, and equipping snow-melting systems with automatic start and shutoff mechanisms.
Within the Ichthys LNG Project, we conduct investigations into freshwater consumption with the aim of reducing consumption in its facilities. We use the findings of these investigations to consider the feasibility of cost-effective approaches for reducing freshwater consumption by reusing water, such as treated wastewater from processing as well as wastewater and condensed steam from power generation facilities.
Use of Seawater
Instead of freshwater, the Ichthys LNG Project’s offshore production facilities use seawater for cooling, and the Naoetsu LNG Terminal uses it for heat exchange in the vaporizer. Mandatory checks of seawater temperature difference between water withdrawal temperature and wastewater temperature as well as residual chlorine levels ensure that the marine environment will not be harmed. These checks also guarantee local laws and regulations and international guidelines are met before the used seawater is discharged back into the sea. At Abu Dhabi, which has high water risks, we use desalinated seawater instead of freshwater such as groundwater.
Wastewater Management of Produced Water
Annual Produced Water Discharge in Japan and Overseas
Unit: thousand ㎥
Produced water from our oil and natural gas projects is reinjected underground, or discharged as wastewater, after being confirmed to comply with the wastewater standards in local and international guidelines. In FY2024, 33% of the total produced water (approximately 0.85 million cubic meters) was reinjected, while the remainder was discharged into rivers or seas after treatment.
Appropriate Treatment and Management of Produced Water
At our operator projects, produced water is injected into injection wells – with maintained integrity – and returned underground, or discharged into rivers and seas after going through water treatment systems and meeting the standards stipulated in the laws and regulations of the respective country or region. Regarding the discharge of produced water into the sea, besides existing regulations targeting dispersed oil in the water, some countries and regions have gone on to adopt regulatory values that also include dissolved hydrocarbon components. For the operation of the Ichthys LNG Project, we also adopt a tertiary advanced processing system that uses Macro Porous Polymer Extraction (MPPE) to remove soluble hydrocarbons before discharging produced water that have met the standard values into the sea.
Education and Training on Water Management
We regularly provide education and training to the staff at our operational sites in Japan to ensure appropriate water management practices and promote efficient water use. We invited an outside lecturer to conduct a seminar on the Mine Safety Act and Water Pollution Prevention Act. We will continue to work on efforts to enhance knowledge and awareness of our staff as necessary.
